In my first post of this 5 part series, the need for innovation was discussed. This post details specific objectives to be considered when creating your innovative vision.

Creating the Innovation Vision
Sometimes the hardest part about making changes is organizing and prioritizing your thoughts to get started. The list below mentions the most critical elements for creating an innovative environment.
Key Innovation Change Objectives: (listed by priority)
-
-
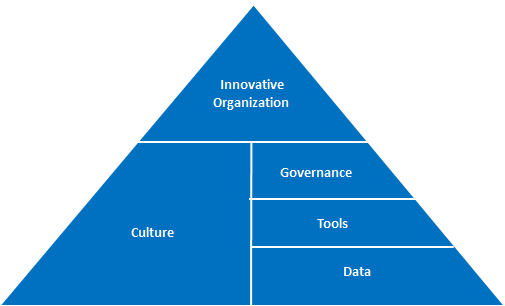
Be an innovative organization:
If your organization’s innovation is too limited at the moment, the first step must be a commitment to being an innovative organization. This can occur only with total buy-in from all leadership. This is a show stopper if not achieved.
-
Create the executive vision and metrics for measurements:
- What are the end goals?
- Operational focus
- Strategic growth areas
- Executive oversight
- KPI’s – this will give the innovators a common direction and path
-
Create the innovation mindset:
-
No organization should rely on technology or ideas generated from the outside. Moreover, there must be no fear of failure or loss of employment for innovation ideas and attempts. As GOOGLE and other entrepreneurial ventures have discovered, to have a great idea you need lots of them.
The challenge will be to encourage people to bring their ideas forward. However, this will require a cultural change not only in how this is achieved going forward but also with collaboration between the current power silos.
-
-
Change the organizational culture:
-
An organization’s culture is rarely defined by one person. It is defined by the type of environment employees work in. Some attributes of an innovate culture include but are not limited to: (How many of these does your organization have?)
-
-
- Dynamic: Embracing continuous change
- Knowledge exchange: Current and new ideas are shared by everyone
- Holistic views: Everyone is working toward a greater good and for survival
- Transparency: This is critical to achieve the proper controls without stifling innovation
- Hire right: It will be important to hire people with the right attitude, energy and integrity. It will also be necessary to remove the dragons (people resistant to change) that may interfere or are more concerned with their individual silos.
- Mentoring: Partnering innovators with experienced entrepreneurs will help achieve greater successes and transparency. The idea is to think through an idea from concept to fruition. Two types of mentors are involved;
- Level 1 mentor – a person who can help think through the submitted idea
- level 2 mentor – an executive or senior manager to provide guidance and oversight if an idea has been selected for further development
- Recognizing cultural change takes time: Disruptive innovation rarely occurs in the short–term. True innovation is a long-term investment of 3-5-10 years or more in people and ideas to obtain the home run payoff. It is similar to starting a business. Few businesses are profitable within the first 3 years.
- Leadership: Any given organization may not have the leaders in place that they will need in order to create an innovative culture. Skill sets needed include staff development, entrepreneurial backgrounds, communications, and the ability to see the strengths in people.
- Peer reviews on ideas: Peers provide feedback on ideas as part of the ideation process
- Time to create: Freedom to run with an approved idea and permitting time for this
-
Define the Governance:
-
What will be the platform for submitting, approving and working on ideas? This is the key for managing ideation and information exchange. It is also crucial for executive oversight, mentoring and obtaining employee engagement.
-
-
Define the Tools:
-
What are the tools to be used for governance and data collection? For example; the selection of a project and monitoring tools. The same tools have to be available to everyone.
-
-
Define Data:
-
How will the innovation engine work? It is critical that this be set up correctly in the beginning. It is at the bottom of the pyramid because without superior data, the rest of the pyramid will crumble.
-
- Where will data be stored?
- Will data be collected and be made available to use for experimentation, trial and error and traceability?
- Where will metrics be stored?
- How will data be transformed into knowledge, intellectual property and know-how?
- Transparency
Once the mindset, innovative culture and framework as a whole have been set up, the next component is to detail out the ideation.
Third Post Subject: Ideation in an Innovative Organization
The third post in this series covers the ideation process from idea submission through the culling, vetting and decision making process. At the end of the series a full downloadable version of How to Create an Innovative Environment in a Dynamic Organization will be available in the Entrepreneur’s Corner.
Previous post in this series are:
How to Create an Innovative Environment in a Dynamic Organization Part 1
